At the core of every electric bike lies the electric motor, the driving force that sets it apart from a traditional bicycle. These motors are designed to provide assistance to the rider's pedalling, making it easier to conquer hills, cover long distances, and ride against headwinds. The primary aim of e-bike motors is to augment human pedal power, not replace it entirely, offering a more enjoyable and less strenuous riding experience.
Electric bike motors operate on a simple principle: they convert electrical energy into mechanical energy to power the bike's movement. Most e-bikes feature a motor integrated into either the front or rear wheel, while others use mid-drive motors, positioned in the bike's frame near the pedals. When the rider starts pedalling, a sensor detects the motion and signals the motor to activate and provide assistance.
There are two main types of e-bike motors: hub motors and mid-drive motors.

Hub motors, also known as wheel motors, are one of the most common types used in e-bikes. These motors are placed in the wheel hub and provides propulsion by spinning the wheel the tyre directly.
- Front Hub Motors: These motors are located in the front wheel of the e-bike. They are relatively simple in design, providing power directly to the front wheel. Front hub motors are easy to install and maintain, but they may affect the bike's balance and handling.
- Rear Hub Motors: Positioned in the rear wheel, these motors offer a more natural riding feel as they do not interfere with the bike's steering. Rear hub motors provide better traction, especially on slippery surfaces, making them suitable for off-road adventures.

Mid-drive motors are installed in the bike's bottom bracket, where the pedals are attached. Unlike hub motors, they interact with the bike's gears, providing more efficient power delivery. Mid-drive motors are known for their torque and performance, making them ideal for tackling steep inclines and rough terrains.
The drivetrain refers to the system that transmits power from the motor to the bike's wheels. In e-bikes, the two main types are mid-drive and hub drive.
1. Mid-Drive: As mentioned earlier, mid-drive motors work in conjunction with the bike's gears. This results in a more natural riding experience, similar to riding a traditional bicycle. The motor's location in the centre of the bike also contributes to better weight distribution, which is beneficial for stability and handling.
2. Hub Drive: Hub motors, whether front or rear, deliver power directly to the wheels without engaging with the bike's gears. While this makes them simpler and more affordable, it can lead to a less dynamic riding experience compared to mid-drive motors.

The e-bike's battery is another critical component, storing the electrical energy needed to power the motor. Lithium-ion batteries are the most commonly used type in e-bikes due to their high energy density, low self-discharge rate, and lightweight design. Battery capacity is measured in watt-hours, indicating how much energy the battery can store.
Chargers for e-bike batteries vary in charging time and compatibility. Some chargers may take a few hours to fully charge the battery, while others may take longer. Make sure to check out our blog post on how long electric batteries last for a more comprehensive run-down on charging times.
Electric bike motors come in various power ratings, typically around the range of 250 watts. The power output determines the level of assistance the motor can provide to the rider. All Progear e-bikes are compliant with Australian road regulations regarding watts and maximum speed. You can also peruse our blog post on where you can ride your e-bike and what is allowed in different states and territories.
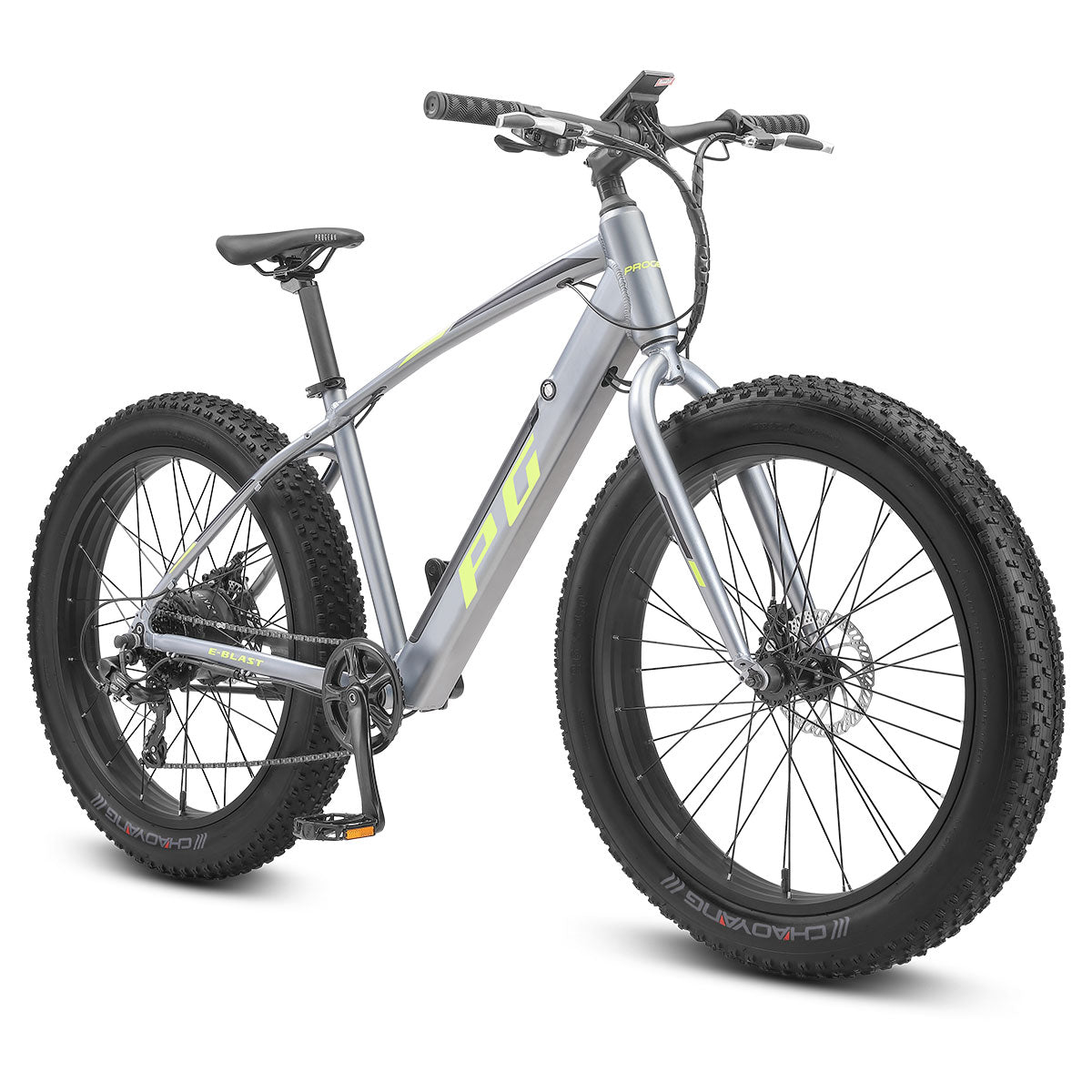
Progear takes pride in offering a wide range of e-bikes tailored to various needs and preferences. Whether you're a city commuter looking for a practical and eco-friendly means of transportation or an adventure seeker ready to explore off-road trails, Progear has an e-bike to suit your lifestyle.

Electric bike motors have transformed the way we approach cycling, making it accessible to a broader audience and enhancing the overall riding experience. Understanding the different types of e-bike motors, how they work, and their benefits is essential in making an informed choice when selecting the perfect e-bike for your needs. Whether you opt for a hub motor for simplicity or a mid-drive motor for superior performance, the joy of riding an electric bike is undeniable. So, hop on and let the electric motor propel you into new cycling adventures!
You can also contact us if you have any questions regarding our range, and our friendly staff will be happy to help you.